Answer: D
The main electrophysiologic properties of adenosine is , via A1 receptor, by stimulation of IKach,Kado
in atrial tissues causing shortening of atrial ERP and hyperpolarization of SA and AV nodal cells.
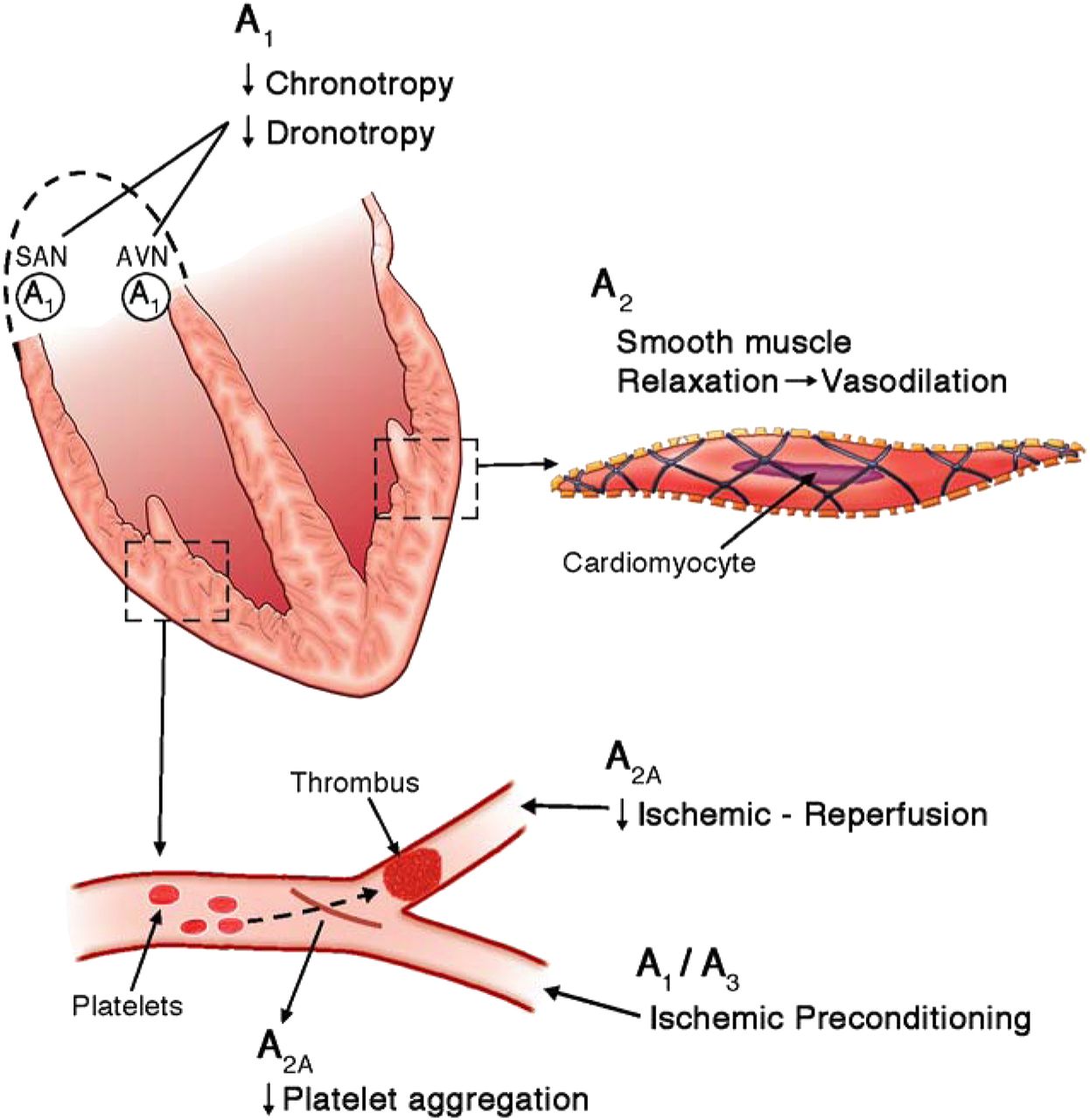
In ventricular myocardium, adenosine suppresses triggered activity by antagonizing catecholaminergic stimulating ICa.
Clinical effects:
Slowing SA and AV node and terminating PSVT.
Terminating catecholaminergic-induced VT.
With potential of initiating of AF/AFL/NSVT after termination of tachycardia.
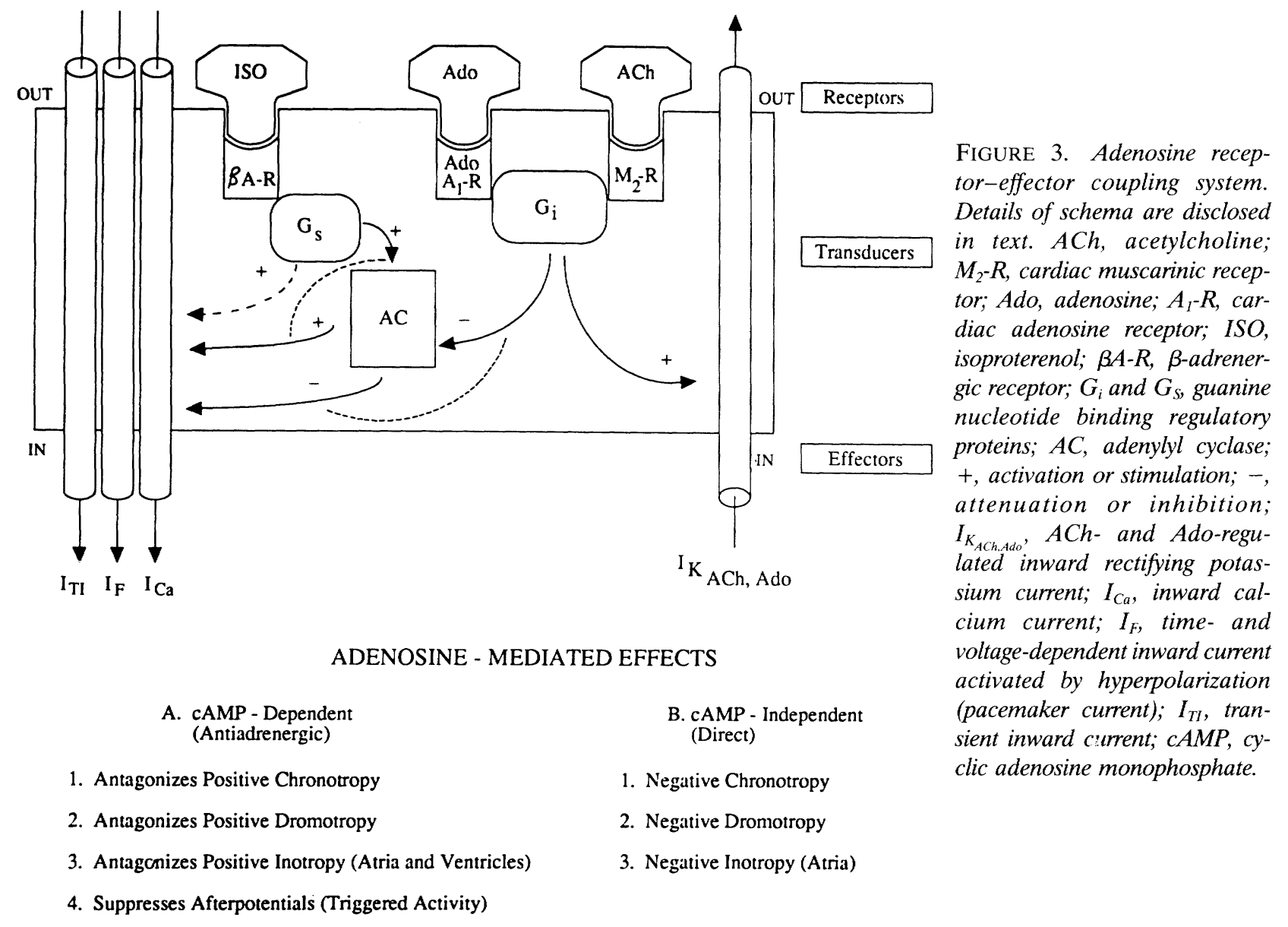

In ventricular myocardium, adenosine suppresses triggered activity by antagonizing catecholaminergic stimulating ICa.
Clinical effects:
Slowing SA and AV node and terminating PSVT.
Terminating catecholaminergic-induced VT.
With potential of initiating of AF/AFL/NSVT after termination of tachycardia.
