SYN
COPE
2018 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope

TRIG
GERS
GERS
Supine position
Sitting
Standing for some period
During normal sleep
Micturation
Defecation
Swallowing
Coughing
Lauging out loud
During and after eating
Head movement
Shaving
During exercise
After exercise
Arm exercise
Startling
Palpitations
During fever
Flashing lights
Sleep deprivation
Straightening from squatting
Fear, pain, instrumentation
Heat, warmth, hot bath
during
ATTACK
ATTACK
Change in vision
Nausea, sweating
Neck and shoulder pain
Shout
Oral automatisms
Cyanosis
Eyes movement
Tongue bitten
Incontinence
Ataxia
Pelvic thrusting
Duration of TLOC
Onset of abn. movement
Sync vs. async movement
Numbers of movement
Pallor
Nausea, sweating
Clear headed
Briefly disoriented
Confused for many minutes
Aching muscles not from bruises
Sleep
The complete initial evalution of syncope includes...
H
- Orthostatic BP
- Physical exam
- ECG
Suggestive Clinical Features
Reflex Syncope
- long Hx of recurrent syncope
- after unpleasant sight, sound, smell, or pain
- prolong standing
- during meal
- being in crowded or hot places
- Prodrome: pallor, sweating, nausea, or vomiting
- with head rotation or pressure on neck
OH (orthostatic hypotension)
- while or after standing
- prolonged standing
- standing after exertion
- after meal
- changes in antihypertensive or diuretic
- autonomic neuropathy or parkinsonism
Cardiac Syncope
- during exertion or when supine
- sudden onset palpitation immediately followed by syncope
- family history of unexplained sudden death at young age
- presence of structural heart disease or coronary artery disease
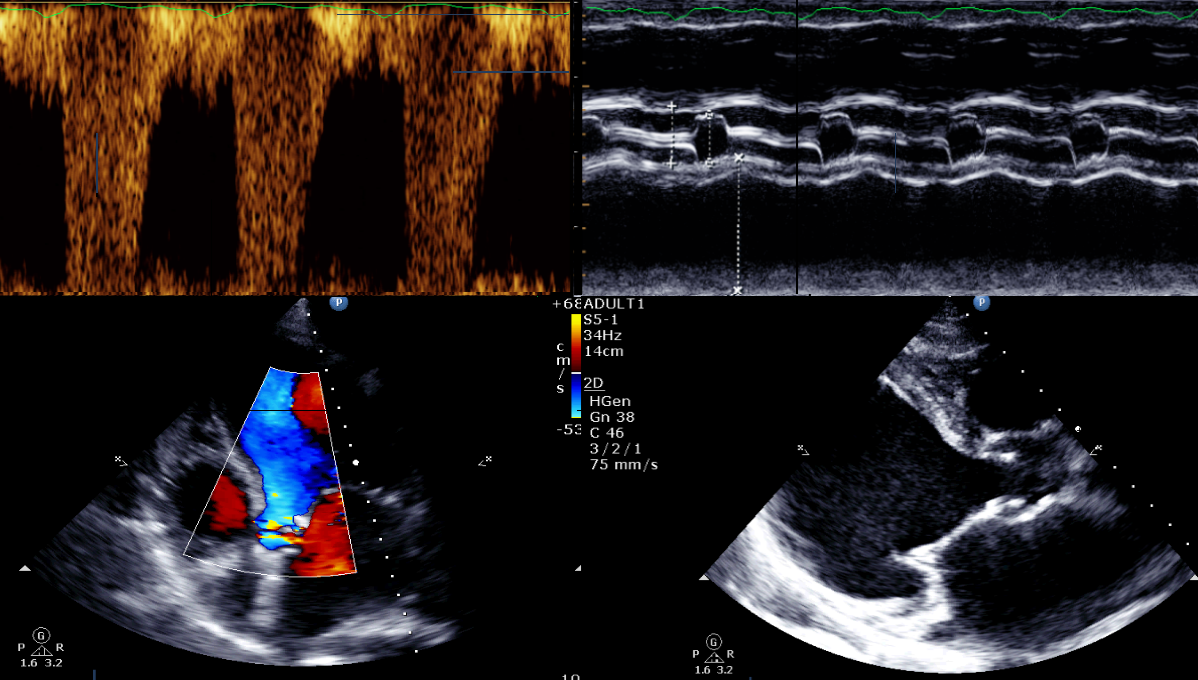
- ECG findings suggesting arrhythmic syncope
(SA/AV block, preexcitation, bifascicular block, LVH, Brugada pattern, TWI in V1-v4, long or short QTc, VT)
Red Flag
Event Detail |
|
Past History |
Severe structural heart disease (Low LVEF, CHF, or Old MI) |
Physical Exam |
|
ECG |
|