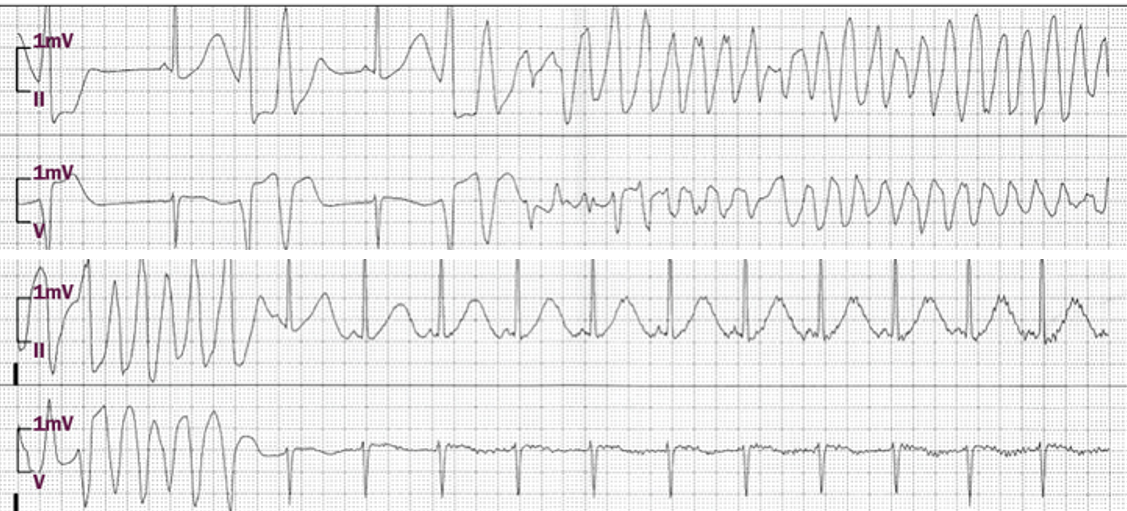
Our Collection
Our Collection
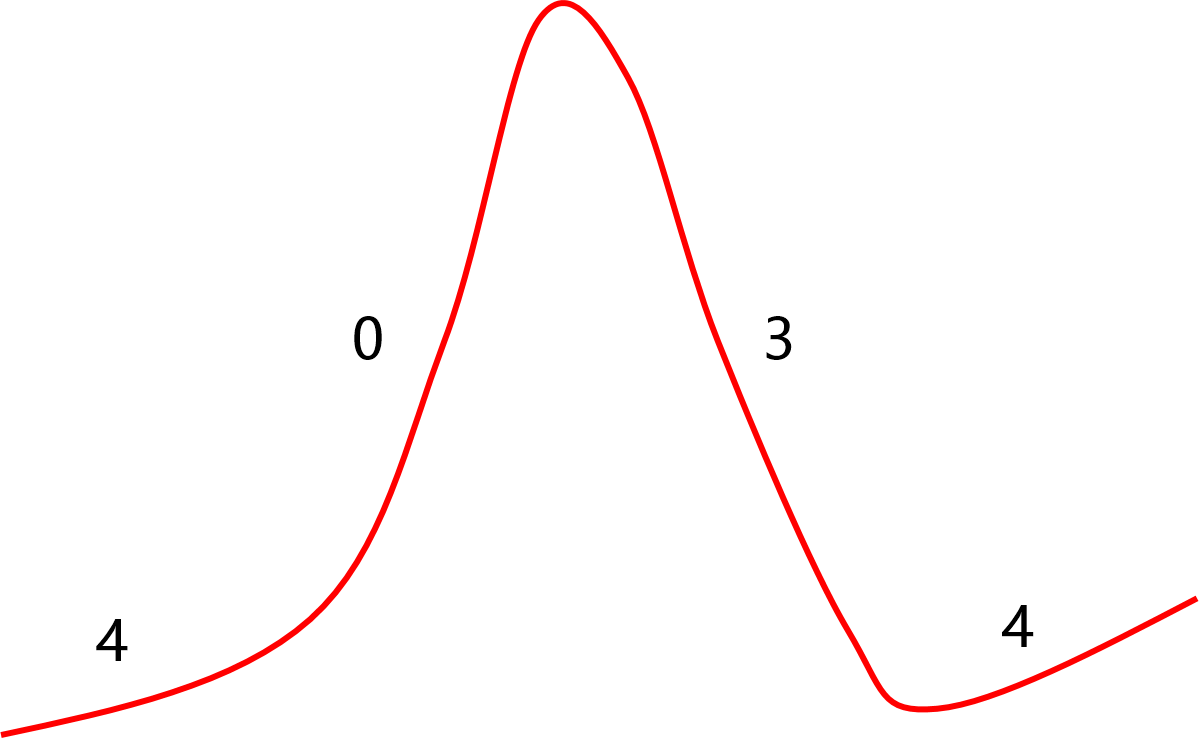
 0
1
2
3
4
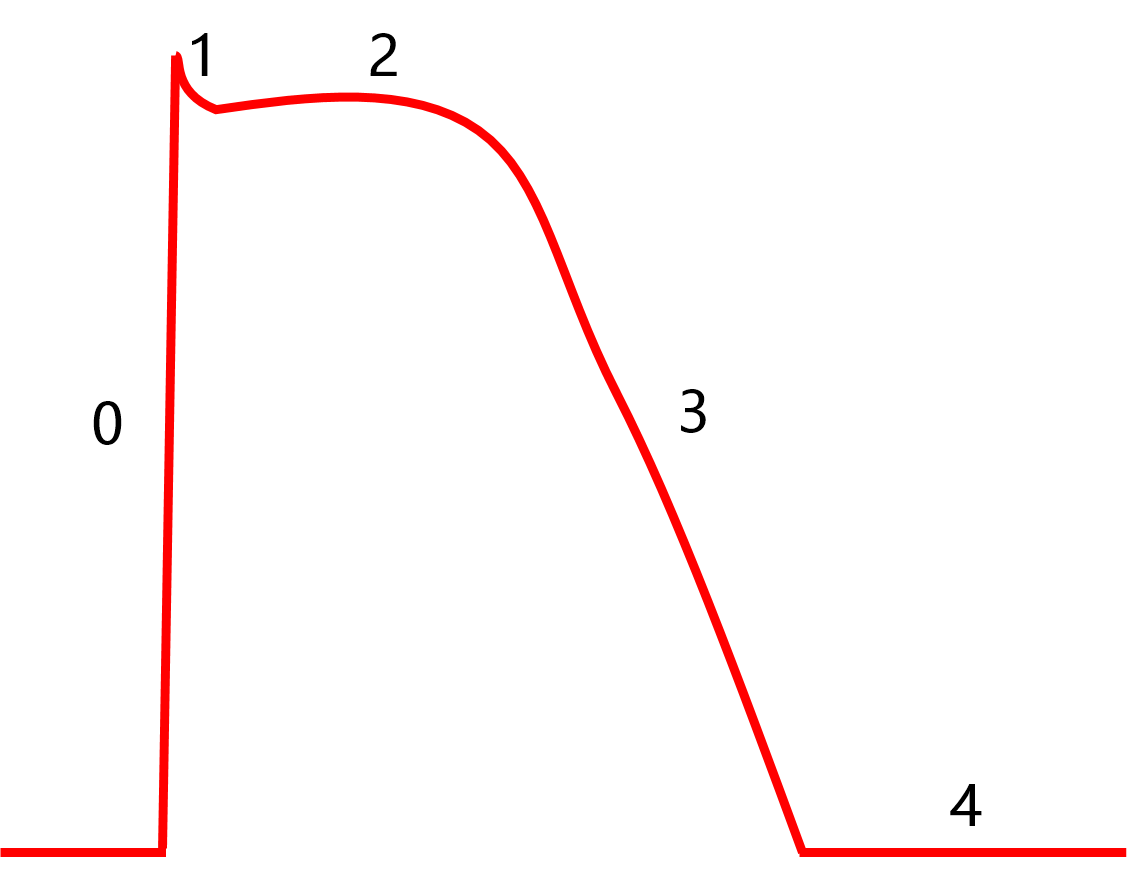
0
1
2
3
4
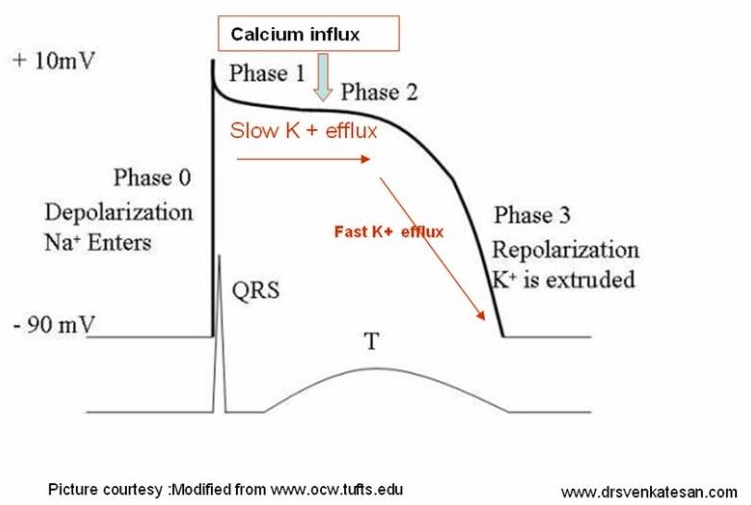
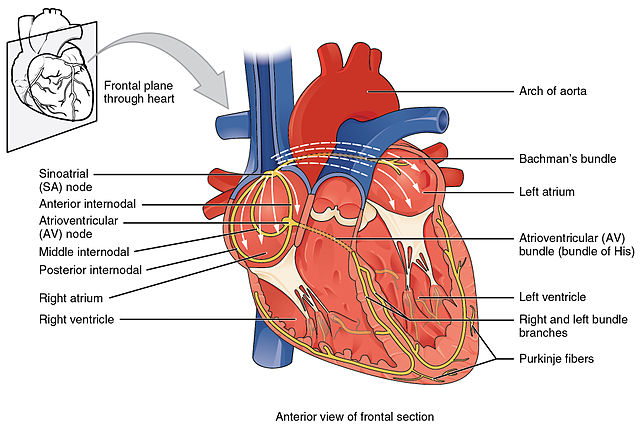
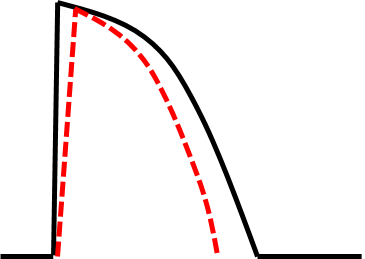
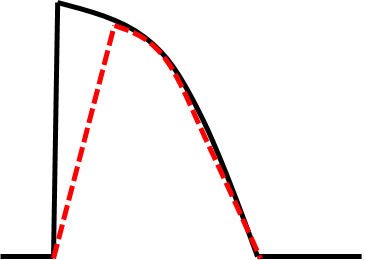
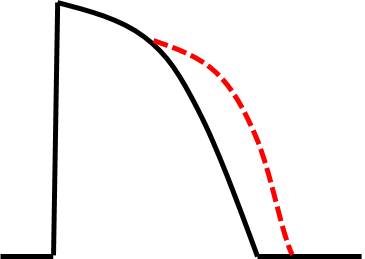
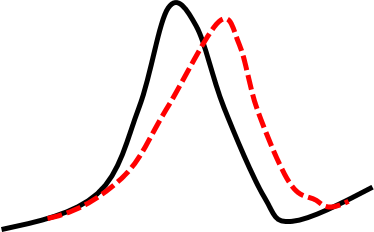
| Properties | Pacemaker cells | non-Pacemaker cells |
|---|---|---|
| Location | SA and AV nodes | Myocardium, His-Purkinje, bypass tract |
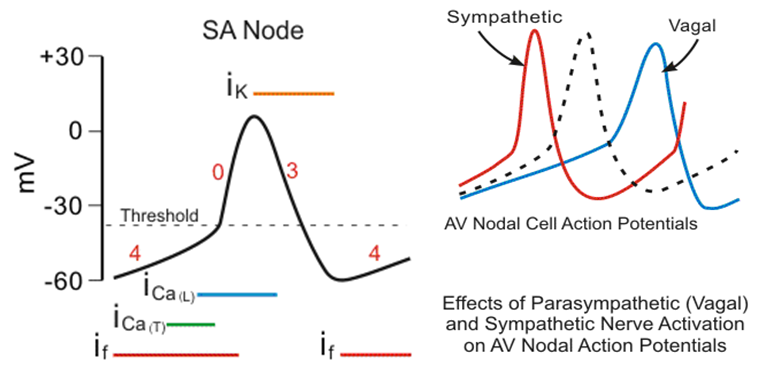
| Normal resting potential | -40 to -65mV | -80 to -95mV |
| Phase 0 current | Primarily Calcium | Sodium |
| Conduction velocity | Slow: 0.01-0.1 m/s | Fast: 0.5-5 m/s |
| Conduction property | Decremental | All or None |

| Pacing |
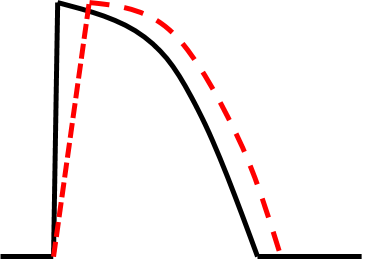
Increase Threshold Class Ic, beta blockers, quinidine hypoxemia, acidosis, alkalosis, hyperglycemia |
Decrease Threshold Epinephrine, Isoproterenol, Atropine, steroids |
| Defibrillation |
Increase Threshold amiodarone, lidocaine, flecainide, sildenafil (Viagra), alcohol |
Decrease Threshold sotalol, dofetilide |